Server Virtualization: A Comprehensive Guide
What is Server Virtualization?
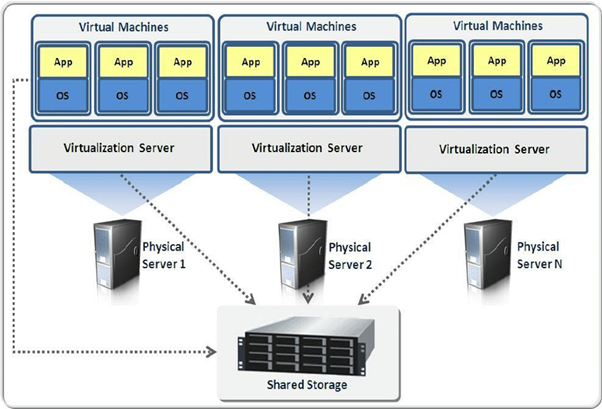
Server virtualization is the process of dividing a physical server into multiple isolated virtual machines (VMs), each running its own operating system (OS) and applications. This is achieved using a hypervisor, which allocates hardware resources dynamically.
How Does Server Virtualization Work?
- Hypervisor (Virtualization Layer)
- Type 1 (Bare-metal): Runs directly on hardware (e.g., VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V, KVM).
- Type 2 (Hosted): Runs atop an OS (e.g., Oracle VirtualBox, VMware Workstation).
- Resource Allocation
- CPU, RAM, storage, and network are partitioned among VMs.
- Enables overcommitment (allocating more resources than physically available).
- Isolation & Security
- VMs operate independently; crashes or malware in one VM do not affect others.
Types of Server Virtualization
| Type | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Full Virtualization | Fully emulates hardware (e.g., VMware ESXi). | Legacy apps, mixed-OS environments. |
| Para-Virtualization | Modified OS for better performance (e.g., Xen). | High-performance computing. |
| OS-Level Virtualization | Shared OS kernel (e.g., Docker, LXC). | Lightweight containers. |
Benefits of Server Virtualization
✔ Cost Savings – Reduce physical hardware needs.
✔ Efficiency – Higher resource utilization (70-80% vs. 10-15% on physical servers).
✔ Disaster Recovery – Snapshots & live migration.
✔ Scalability – Spin up VMs in minutes.
✔ Isolation – Secure multi-tenant environments.
Popular Virtualization Platforms
- VMware vSphere (Enterprise-grade).
- Microsoft Hyper-V (Windows-centric).
- KVM (Kernel-based VM) (Open-source, Linux-native).
- Proxmox VE (Open-source, supports VMs & containers).
Use Cases
- Data Centers – Consolidate servers.
- Cloud Computing – Basis for IaaS (AWS, Azure).
- Development/Testing – Isolated sandbox environments.
- Legacy App Support – Run outdated OSes securely.
Challenges
⚠ Performance Overhead – Hypervisor adds latency.
⚠ Complexity – Requires skilled management.
⚠ Licensing Costs – Proprietary solutions (e.g., VMware).
Conclusion
Server virtualization maximizes hardware efficiency while enabling flexibility, security, and scalability. Whether for enterprises, cloud providers, or developers, it’s a cornerstone of modern IT infrastructure.
(Need deeper technical details? Ask about specific hypervisors or benchmarks!) 🚀

